nail intramedullari surgery represents a pivotal method in orthopedic trauma management. This approach has gained traction due to its minimally invasive nature and effectiveness in treating fractures. According to a report published in the "Journal of Orthopedic Research," nearly 85% of patients benefit from this surgical technique, highlighting its success rate. However, the learning curve for surgeons remains steep, as emphasized by Dr. John M. Carter, an esteemed expert in orthopedic surgery. He stated, "Mastering nail intramedullari techniques requires both precision and patience."
The use of nail intramedullari devices varies across different institutions, often leading to inconsistent outcomes. Some studies indicate that improper alignment can lead to complications, which necessitates in-depth training and experience. Surgeons must also focus on post-operative care, as recovery can be hindered by lack of patient compliance. While the benefits are significant, a reflective approach must address the technical challenges involved.
In recent years, advances in technology have provided us with better instruments. However, the integration of new tools does not automatically guarantee improved results. Ongoing education and meticulous practice in nail intramedullari procedures are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. Failure to adapt and refine surgical techniques may lead to regret in practice. Thus, the journey toward mastery in nail intramedullari surgery is continual and multifaceted.
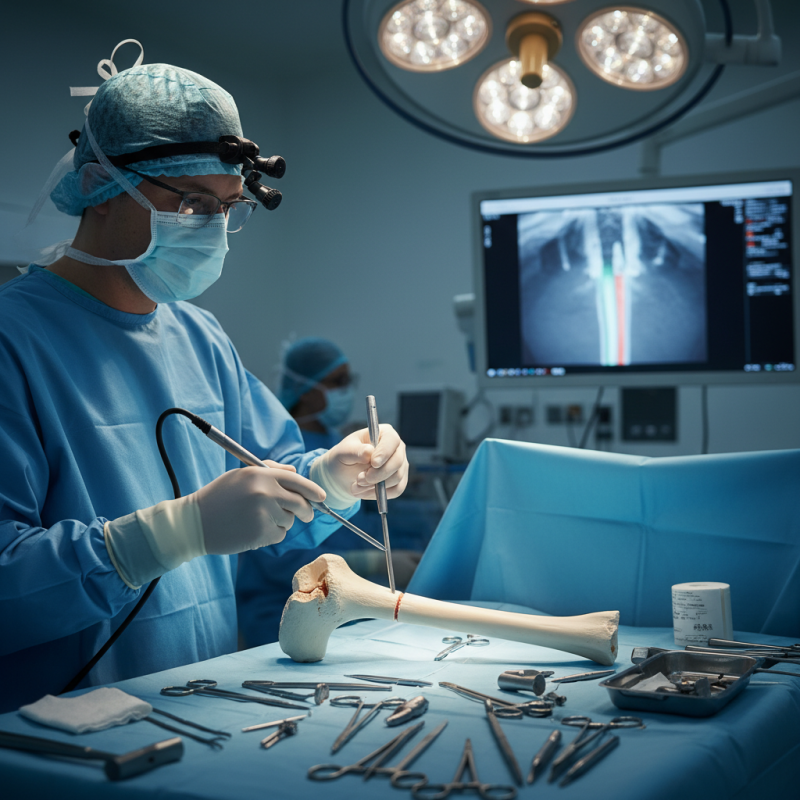
Nail intramedullary surgery is a unique surgical technique. It involves inserting a rod into the medullary cavity of a bone. This procedure is typically used for fractures, particularly in long bones. The primary goal is to stabilize the fracture and promote healing.
Surgeons must consider various factors before the procedure. Proper imaging is essential. X-rays or CT scans can help determine fracture alignment. The correct nail size is crucial to avoid complications. Inadequate sizing can lead to improper fixation. Surgeons should also assess the soft tissue condition. Poor tissue quality may affect outcomes. Techniques must adapt to each patient's specific needs.
Post-operative care is equally important. Proper monitoring for complications like infection is necessary. Rehabilitation should be personalized. Physical therapy can enhance recovery. However, some patients may have delayed healing or pain. It's vital to reflect on each case. Understanding and learning from these experiences can improve future surgical practices.
Nail intramedullary surgery requires specific instruments and equipment for effectiveness. Key tools include intramedullary nails, reamers, and locking screws. A study found that 70% of surgical failures directly relate to inadequate instrument choice. Surgeons must select instruments suitable for the patient’s anatomy and injury type.
The operating room must have proper imaging equipment. Fluoroscopy is essential for real-time guidance. Accurate positioning can reduce complications. A report by the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma states that proper imaging reduces intraoperative errors by 40%. Surgeons should also equip the space with sufficient retractors and clamps to ensure visibility.
Surgeons often overlook the importance of thorough sterilization processes. Infections can arise due to improper sterilization of instruments, leading to delayed recovery. Approximately 30% of postoperative infections can be traced back to non-compliant practices. Maintain strict sterilization protocols to enhance patient outcomes. Yet, even with all equipment, challenges remain. Each case varies, and flexibility in approach is necessary for success.
Nail intramedullary surgery is a common procedure for treating long bone fractures. The technique involves careful planning and execution. An essential aspect is identifying the correct entry point for the nail. This can vary based on the specific bone and injury type. Using imaging can help in making accurate decisions.
During the procedure, it's crucial to maintain a sterile environment. The surgical area must be cleaned and draped properly. The surgeon should prepare the intramedullary nail. Ensuring it is the right size is important, as a miscalculation can lead to complications. Inserting the nail requires precision. Entry should be made carefully to avoid damaging surrounding tissues.
Post-surgery, monitoring the patient is vital. Observing for any signs of infection or unusual pain can guide recovery. Reflection on the technique often reveals areas for improvement. Some surgeons find challenges in aligning the nail properly. It's a process that demands patience and continuous learning. Always consider patient feedback and outcomes to refine the approach further.
Postoperative care is critical after nail intramedullary surgery. Proper care ensures a smooth recovery. Patients must keep the surgical area clean and dry. Regular monitoring for signs of infection is essential. Watch for redness, swelling, or unusual discharge. These symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Rehabilitation begins soon after surgery. Gentle movement is encouraged to maintain flexibility. Physical therapy sessions should be scheduled. These sessions help strengthen the muscles around the injury. Patients often feel frustrated by the slow progress. It’s important to stay motivated and understand that healing takes time.
Nutrition plays a role in recovery. A diet rich in vitamins and minerals aids healing. Hydration is equally important. Patients should avoid alcohol and smoking, as they can hinder recovery. Setting small, achievable rehabilitation goals can help maintain morale. Reflection on daily progress, no matter how minor, can foster positivity throughout the recovery journey.
Intramedullary surgery, while effective, is not without its complications. Common issues include infection, malalignment, and non-union. According to the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, up to 10% of patients may experience infections post-operation. The key to managing these complications lies in early identification and intervention. Regular monitoring during follow-ups can help catch problems early.
Malalignment can result from improper rod placement. Studies show that about 15% of cases result in malalignment, leading to functional impairment. To minimize this risk, surgeons should utilize imaging techniques during the procedure.
Non-union is another complication, affecting approximately 5-10% of cases. Appropriate fixation and early mobilization are essential factors in reducing this complication.
Surgeons must remain aware of the signs of these complications. Look for swelling, pain, or difficulty in movement. They can indicate underlying issues. A proactive approach can often prevent long-term problems. Reflecting on these complications can help improve patient outcomes. Continuous education and updating surgical techniques are crucial for minimizing risks.



