In the world of construction and heavy lifting, selecting the right wire rope is crucial. As John Smith, a wire rope specialist, once said, "Choosing the correct wire rope can make or break a project." Different applications demand various wire rope types. For instance, some tasks require high tensile strength, while others need flexibility.
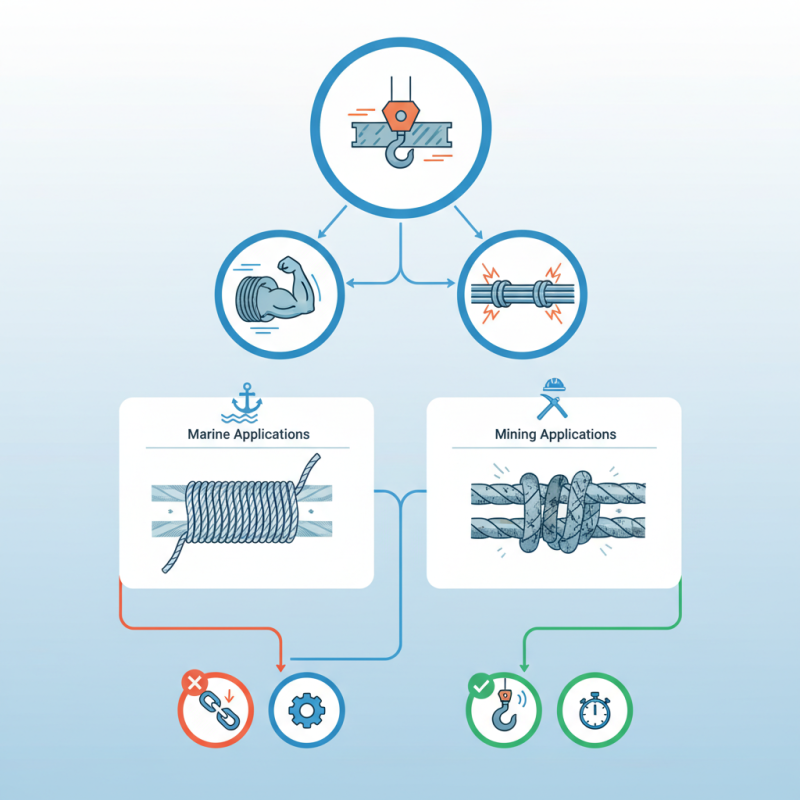
Different industries utilize wire ropes in unique ways. In marine applications, galvanized wire ropes resist saltwater corrosion. For mining, wire ropes must withstand extreme wear and tear. This specificity highlights why understanding each type's properties is essential. Choices made in the early stages can lead to problems later on.
Many users overlook critical details. The wrong wire rope may lead to accidents or failures. While some might rush the decision process, the implications are severe. Reflecting on these choices is vital. The right wire rope enhances safety and efficiency, making it an indispensable element in various applications.
Wire ropes are crucial in various industries. Each type has unique specifications that make it suitable for specific applications. Steel wire ropes are the most common. They offer high tensile strength and flexibility. This makes them ideal for lifting heavy loads.
Another type is plastic-coated wire rope. This type offers protection against corrosion. It’s useful in marine environments. However, it may not have the same strength as steel ropes. It’s essential to consider the environment when choosing a rope type.
Galvanized wire rope provides extra durability. It resists rust and wear. Yet, it can be heavier and stiffer than other types. This can be a disadvantage in some applications. Always evaluate the specific needs before making a decision. Each wire rope has its strengths and weaknesses, demanding careful selection for optimal performance.
| Wire Rope Type | Material | Diameter (mm) | Breaking Strength (kN) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6x19 Class | Steel | 6, 8, 10 | 40-150 | Construction, Mining |
| 6x36 Class | Steel | 10, 12, 14 | 80-200 | Crane, Lifting |
| 7x19 Construction | Galvanized Steel | 1.5, 2, 3 | 10-40 | Winching, Rigging |
| Fiber Core Wire Rope | Steel with Synthetic Core | 8, 10, 12 | 50-100 | Marine, Offshore |
| Rotation Resistant | Steel | 10, 14, 18 | 200-400 | Heavy Lifting, Oil & Gas |
Choosing the best wire rope type depends on its application. There are various types, each suited for specific tasks. For instance, stainless steel wire ropes resist corrosion and are perfect for maritime environments. According to industry reports, nearly 50% of wire ropes fail due to environmental factors. This highlights the need for proper selection.
Construction sites often utilize galvanized wire ropes. They provide excellent strength for lifting heavy materials. In this setting, rope diameter and construction enhance load-bearing capacity. The most common diameters range from 6 mm to 16 mm, depending on the application. However, some users overlook the importance of regular inspections.
Tips: Always check for wear and tear. It’s crucial for safety. In industrial settings, wire ropes exposed to high temperatures require special materials. Workers sometimes use standard ropes, risking performance. Be cautious with your choices. Each application hosts unique demands. Make well-informed decisions to ensure efficiency and safety.
Choosing the right wire rope is crucial for any application. Several factors dictate this choice. Load capacity is one of the most critical aspects. Heavy loads require stronger materials. Reports show that wire ropes with a higher tensile strength, around 1800 MPa, can support significantly larger weights. The diameter of the rope also affects its strength. A thicker rope can often bear more load but may be less flexible.
Environment plays a significant role too. Ropes used in corrosive environments need special coatings. Saltwater, for example, can degrade standard steel quickly. According to industry standards, stainless steel ropes resist corrosion but may lack the same tensile strength as carbon steel. Temperature changes can also impact performance. High temperatures can weaken some materials, while low temperatures can make others brittle.
Lastly, the application itself cannot be overlooked. Cranes, elevators, and marine applications each have specific requirements. A flaw in rope selection can lead to operational hazards. Failure statistics show that around 15% of accidents occur due to inappropriate wire rope use. Reflecting on this can provide insights for better choices in the future.
Proper maintenance of wire ropes is essential for safety and longevity. According to industry reports, up to 50% of wire rope failures are due to inadequate maintenance. Regular inspections can help catch and address issues before they escalate. Check for visible wear, kinking, or corrosion regularly. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers recommends performing these checks at least once a month.
Cleaning wire ropes is crucial to their performance. Dirt and debris can cause significant wear over time. A simple rinse with clean water can go a long way. After cleaning, ensure proper lubrication. Lubricants help reduce friction and protect against corrosion. It’s advisable to use the correct type of lubricant recommended for the specific rope material. However, over-lubrication can lead to a messy buildup.
Additionally, environmental factors play a role in wire rope wear. Extreme temperatures and moisture can accelerate deterioration. Storing wire ropes in a dry, temperature-controlled environment can mitigate some of these issues. Yet, many operations overlook this aspect, leading to premature failure. Understanding these factors is key. Regular maintenance checks and appropriate storage can significantly enhance wire rope performance and lifespan.
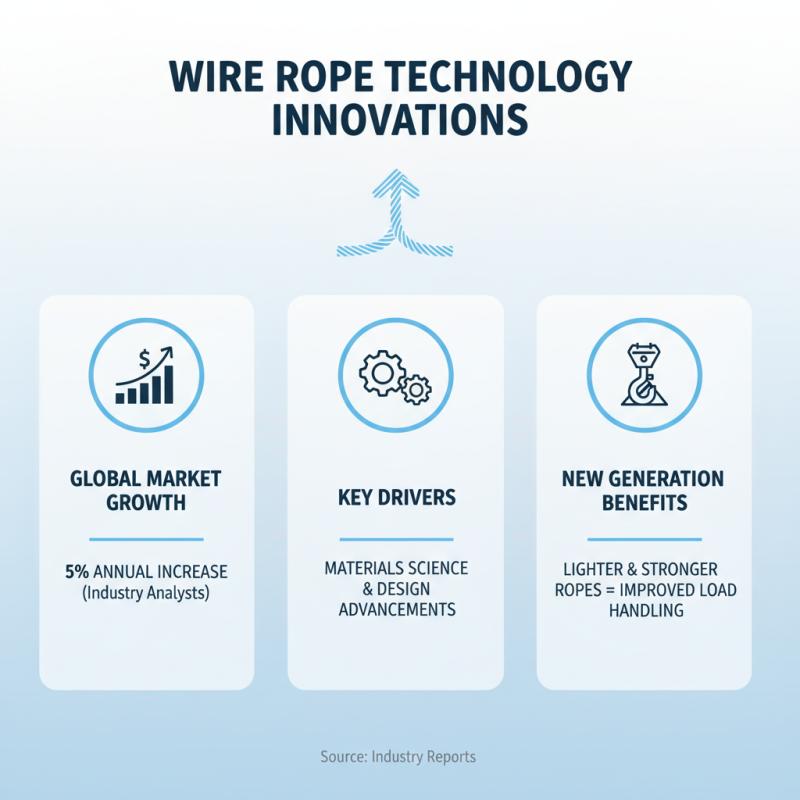
Innovations in wire rope technology are shaping various industries. The global wire rope market is projected to grow by 5% annually, as reported by industry analysts. This growth is driven by advancements in material science and design. New types of wire ropes are lighter yet stronger, facilitating better load handling.
Recent studies indicate that synthetic fibers are increasingly replacing traditional steel cables. These materials offer resistance to corrosion and fatigue, leading to longer service life. For instance, high-strength polyethylene ropes can be three times lighter and just as strong as their steel counterparts. This shift is evident in maritime applications, where weight savings are crucial.
However, not all innovations meet operational needs. Some new materials may lack the abrasion resistance required in harsh environments. The challenge lies in balancing performance with durability. Manufacturers are working on hybrid ropes, blending steel and synthetic fibers. This combination aims to enhance properties but is still in development stages. Overall, the evolution of wire rope technology poses both opportunities and challenges for industries worldwide.